Building an Agentic AI System with CrewAI
Learn how we built an agent using CrewAI to write a blog about Agentic AI. Now that’s some recursion at work!
About the Authors:
Arun Subramanian: Arun is an Associate Principal of Analytics & Insights at Amazon Ads, where he leads the development and deployment of innovative insights to optimize advertising performance at scale. He has over 12 years of experience and is skilled in crafting strategic analytics roadmaps, nurturing talent, collaborating with cross-functional teams, and communicating complex insights to diverse stakeholders.
Manisha Arora: Manisha is a Data Science Lead at Google Ads, where she leads the Measurement & Incrementality vertical across Search, YouTube, and Shopping. She has 11+ years of experience in enabling data-driven decision-making for product growth.
Introduction
In our previous blog, we introduced the concept of Agentic AI, exploring how iterative workflows—such as reflection, planning, and multi-agent collaboration—enhance the adaptability and effectiveness of AI systems. We demonstrated how Agentic AI can outperform traditional approaches by using multi-step processes for smarter decision-making.
In this follow-up, we dive deeper into CrewAI, a framework designed to simplify the creation and management of AI agents and multi-agent systems. Specifically, we’ll explore how CrewAI can be used to build intelligent systems that collaborate seamlessly to accomplish complex tasks. We’ll also demonstrate how we used this framework to generate an article using a multi-agent system, showcasing its real-world application and potential.
Let’s dive in!
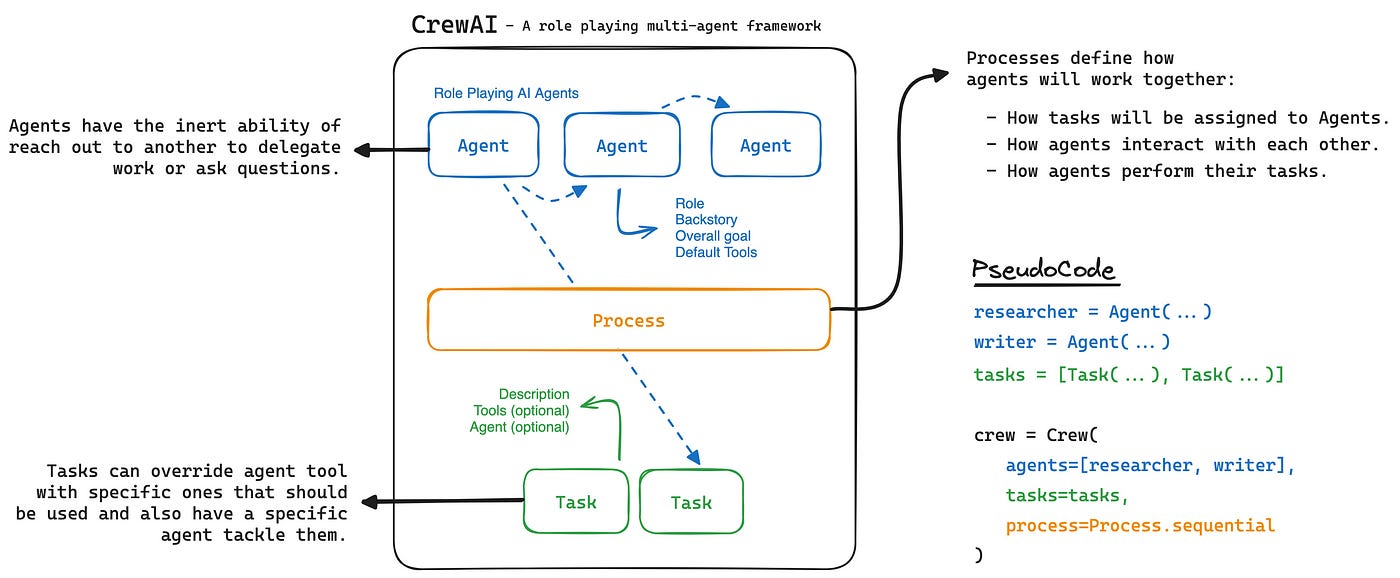
The CrewAI Framework
CrewAI is a powerful framework designed to streamline the creation of AI agents and multi-agent systems. Its primary focus is on simplifying the development of intelligent systems capable of interacting with each other and their environment to accomplish complex goals. Below is an introduction to the core concepts of CrewAI:
Core Concepts:
Agents: The foundational building blocks of CrewAI. Agents are autonomous entities that can perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions based on those decisions.
Tools: Agents use tools to interact with the world around them. These tools can range from simple functions (such as performing calculations or querying a database) to more complex external systems (such as web browsers or APIs).
Tasks: Each agent is assigned specific tasks, which define the goals they need to achieve. Tasks can vary in complexity, and agents may collaborate to complete them efficiently.
Reference image: https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:1400/0*SH1iABY6Oswg0yU5.png
Key Features and Benefits:
Simplified Agent Development: CrewAI provides abstractions and tools that make it easier to define agents, their capabilities, and their interactions. This eliminates the need to handle many low-level technical details, allowing developers to focus on higher-level design.
Multi-Agent Coordination: CrewAI excels in managing interactions between multiple agents. It provides mechanisms for agents to communicate, share information, and coordinate their actions effectively, enabling smooth collaboration.
Tool Management: The framework simplifies the process of integrating and managing tools for agents. This makes it easy to extend the capabilities of your agents.
Flexibility and Extensibility: CrewAI is designed to be flexible and extensible, allowing you to customize it to fit your specific needs.
Focus on Practical Applications: Unlike frameworks that prioritize theoretical research, CrewAI is specifically geared toward building practical, real-world AI applications.
Agentic AI Setup for Generating ML Blog Articles
To illustrate the power of CrewAI, we employed a multi-agent system to generate a blog article about Agentic AI. This system consisted of three key agents: Planner, Writer, and Editor, all leveraging the YouTubeVideoSearchTool() to gather relevant information.
Agents (Role, Goal, Backstory):
Planner Agent: Responsible for creating a structured plan for the article based on the topic ("Agentic AI"). The Planner sets the direction and structure for the content.
Writer Agent: This agent takes the plan created by the Planner and writes the actual content of the article.
Editor Agent: After the article is written, the Editor reviews and edits it for clarity, coherence, and accuracy, ensuring the content meets the desired standards.
Tasks (Description, Expected Output):
Plan Task: Define the structure and goals for the article. The expected output is a detailed outline that organizes the content flow.
Write Task: Develop the article content based on the plan. The expected output is a draft article that follows the established structure.
Edit Task: Review the content for coherence and clarity. The expected output is the final polished article ready for publication.
Tools:
YouTubeVideoSearchTool(): This tool allows agents to conduct a Retrieve and Generate (RAG) process based on YouTube video content. Both the Planner and Writer agents have access to this tool to gather relevant information and refine the article content.
Crew Setup:
To execute the tasks, we brought together the agents, tools, and tasks in a well-organized workflow. CrewAI allows you to set up whether tasks are executed sequentially or in parallel, and defines how agents collaborate to complete these tasks. Once the crew is set up, it can be initiated with the necessary inputs, and the agents begin performing their tasks.
All codes are hosted on this GitHub repo
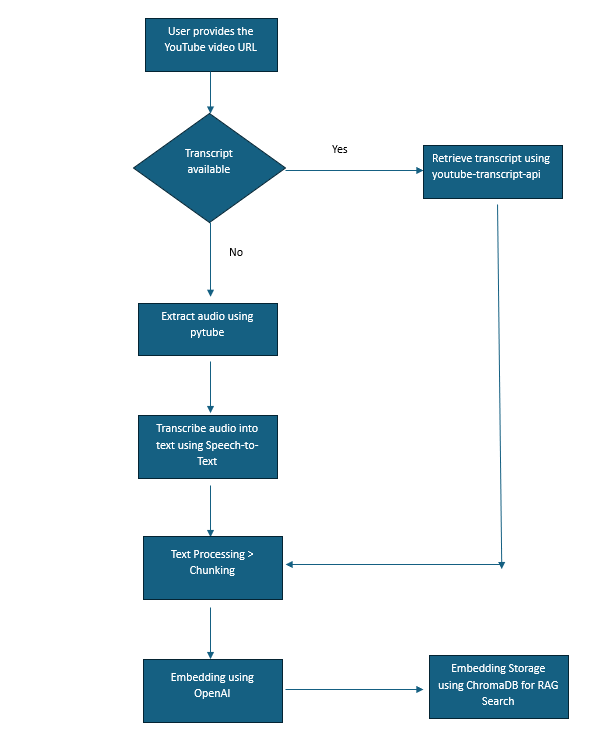
Dive Deep into the Video-to-RAG Process:
Here’s a closer look at how CrewAI’s YouTubeVideoSearchTool() enabled the agents to generate the article:
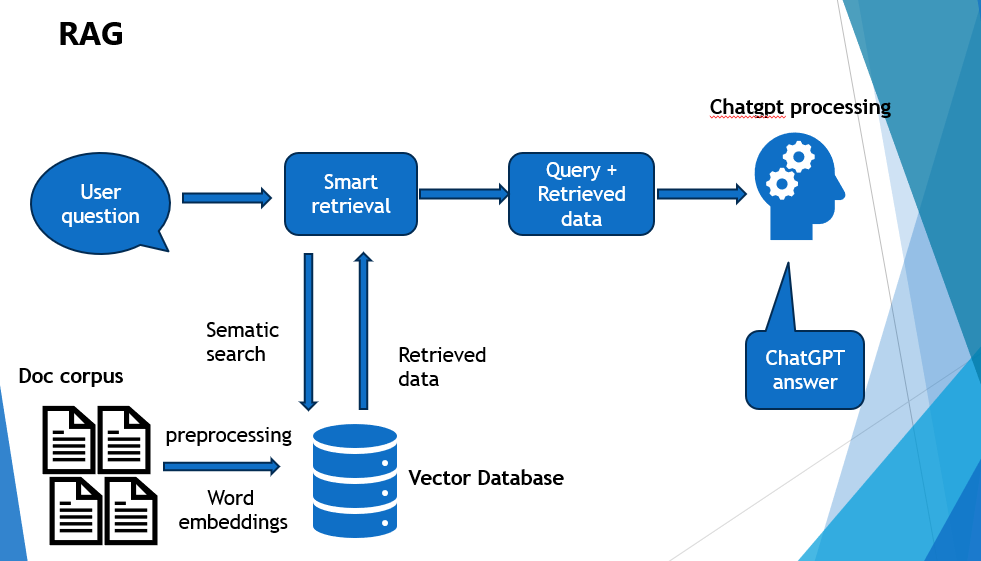
At the core of the RAG process is the use of text stored as embeddings in a vector database for similarity search. When a user enters a query, its embedding is used to search for relevant information from the database. This retrieved context is then augmented with the user query and passed on to the large language model (LLM), which generates a more accurate, relevant, and grounded response.
Step-by-Step Process:
Video to Text Embeddings: The YouTube videos are transcribed into text and converted into embeddings.
RAG Search: The embeddings are used in a similarity search to retrieve context relevant to the query, which is then passed to the LLM to generate a response.
Reference Image
https://miro.medium.com/v2/resize:fit:981/1*FdDtFV3XmzCw0aU93yYrvA.png
Key Takeaways:
Simplified Agent Development: CrewAI simplifies both agent creation and multi-agent coordination, enabling the development of complex AI systems with ease.
Practical Applications: By utilizing tools like YouTubeVideoSearchTool(), CrewAI empowers agents to gather and process information from external sources (e.g., YouTube videos), enriching the content generation process.
Structured Workflow: Breaking the process into distinct phases (planning, writing, and editing) with clear tasks ensures smooth agent collaboration and provides transparency into the decision-making process of the LLM.
A huge THANK YOU to Manisha Arora for co-authoring this newsletter with me.